
Python:传统ARIMA及SARIMAX实现
发布于2019-08-07 11:40 阅读(5907) 评论(0) 点赞(3) 收藏(1)
传统ARIMA步骤:
加载数据:模型建立的第一步当然是加载数据集。
预处理:取决于数据集,预处理的步骤将被定义。这将包括创建时间戳、转换日期/时间列的dType、制作系列单变量等。
使系列平稳:为了满足假设,有必要使系列平稳。这将包括检查序列的平稳性和执行所需的变换。
确定值:为了使序列平稳,将执行差值操作的次数作为d值
创建ACF和PACF图:这是ARIMA实施中最重要的一步。ACF PACF图用于确定我们的ARIMA模型的输入参数。
确定p和q值:从前一步的图中读取p和q的值
拟合ARIMA模型:使用处理后的数据和我们先前步骤计算的参数值,拟合ARIMA模型
预测集上的预测值:预测未来价值
计算MSE或者RMSE:为了检查模型的性能,使用验证集上的预测和实际值检查MSE或者RMSE值
在实现的过程使用SARIMAX实现,这是一个包含季节趋势因素的ARIMA模型。
下面直接上代码:
data:直接采用 facebook 的prophet时序算法中examples的数据,可以在git上下载。
begin:
# Load data
df = pd.read_csv('data/example_air_passengers.csv')
df.ds = pd.to_datetime(df.ds)
df.index = df.ds
df.drop(['ds'], axis=1, inplace=True) y
ds
1949-01-01 112
1949-02-01 118
1949-03-01 132
1949-04-01 129
1949-05-01 121
# Resampling
df_month = df.resample('M').mean()
print(df_month.head())
y
ds
1949-01-31 112
1949-02-28 118
1949-03-31 132
1949-04-30 129
1949-05-31 121# 拆分预测集及验证集
df_month_test = df_month[-5:]
print(df_month_test.tail())
print('df_month_test', len(df_month_test))
df_month = df_month[:-5]
print('df_month', len(df_month))# PLOTS
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[15, 7])
plt.suptitle('sales, mean', fontsize=22)
plt.plot(df_month.y, '-', label='By Months')
plt.legend()
# plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 看趋势
plt.figure(figsize=[15, 7])
sm.tsa.seasonal_decompose(df_month.y).plot()
print("air_passengers test: p={}".format( adfuller(df_month.y)[1]))
# air_passengers test: p=0.996129346920727
# Box-Cox Transformations ts序列转换
df_month['y_box'], lmbda = stats.boxcox(df_month.y)
print("air_passengers test: p={}".format(adfuller(df_month.y_box)[1]))
# air_passengers test: p=0.7011194980409873下一步观察季节差分及趋势差分,找出m及d。
# Seasonal differentiation
# 季节性差分确定sax中m参数
df_month['y_box_diff'] = df_month['y_box'] - df_month['y_box'].shift(12)
# 做个例子
最后得到的pvalue test diff13: p=0.000418 证明序列是稳定的。
下面进行模型选择及预测输出指标:
# SARIMAX参数说明
'''
趋势参数:(与ARIMA模型相同)
p:趋势自回归阶数。
d:趋势差分阶数。
q:趋势移动平均阶数。
季节性参数:
P:季节性自回归阶数。
D:季节性差分阶数。
Q:季节性移动平均阶数。
m:单个季节期间的时间步数。
'''# Initial approximation of parameters
Qs = range(0, 3)
qs = range(0, 3)
Ps = range(0, 3)
ps = range(0, 3)
D = 1
d = 1
parameters = product(ps, qs, Ps, Qs)
parameters_list = list(parameters)
# list参数列表
print('parameters_list:{}'.format(parameters_list))
print(len(parameters_list))
results = []
best_aic = float("inf")
for parameters in parameters_list:
try:
# SARIMAX 训练的时候用到转换之后的ts
model = sm.tsa.statespace.SARIMAX(df_month.y_box, order=(parameters[0], d, parameters[1]),
seasonal_order=(parameters[2], D, parameters[3], 12)).fit(disp=-1)
except ValueError:
print('wrong parameters:', parameters)
continue
aic = model.aic
if aic < best_aic:
best_model = model
best_aic = aic
best_param = parameters
results.append([parameters, model.aic])
result_table = pd.DataFrame(results)
result_table.columns = ['parameters', 'aic']
print(result_table.sort_values(by='aic', ascending=True).head())
print(best_model.summary())
# Model: SARIMAX(0, 1, 1)x(1, 1, 2, 12) 得到 best_model 同时可以观察acf(resid)
sm.graphics.tsa.plot_acf(best_model.resid[13:].values.squeeze(), lags=48, ax=ax)
# 下图是对残差进行的检验。可以确认服从正太分布,且不存在滞后效应。
best_model.plot_diagnostics(lags=30, figsize=(16, 12))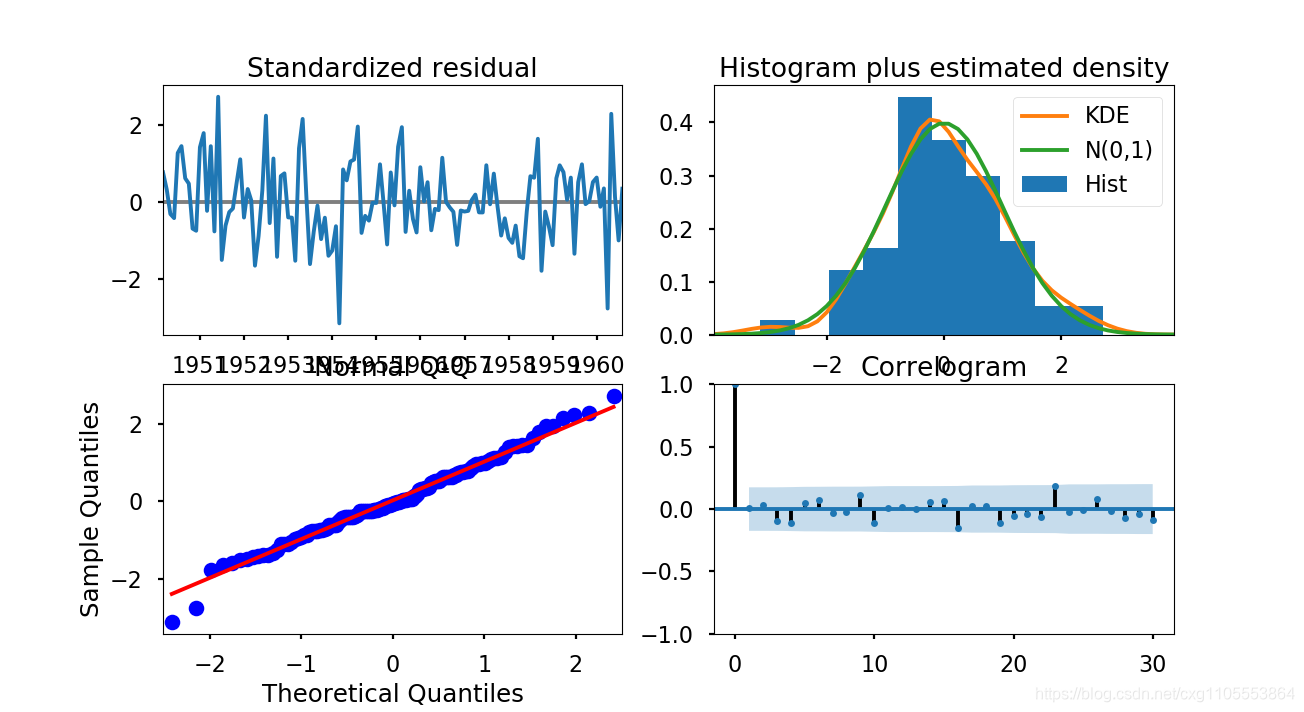
验证结束之后最后对测试集预测并输出指标mse及rmse
df_month2 = df_month_test[['y']]
# best_model.predict() 设定开始结束时间
# invboxcox函数用于还愿boxcox序列
df_month2['forecast'] = invboxcox(best_model.forecast(steps=5), lmbda)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,7))
df_month2.y.plot()
df_month2.forecast.plot(color='r', ls='--', label='Predicted Sales')
plt.show()
# 获取mse
print('mean_squared_error: {}'.format(mean_squared_error(df_month2.y, df_month2.forecast)))
最后结果:#mean_squared_error: 90.93184037574731
结尾:
TS模块后续陆续更新auto_arima及lstm相应的概述及代码实现。
所属网站分类: 技术文章 > 博客
作者:gg
链接:https://www.pythonheidong.com/blog/article/10441/4dc7f8e82bfcb62462fc/
来源:python黑洞网
任何形式的转载都请注明出处,如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
昵称:
评论内容:(最多支持255个字符)
---无人问津也好,技不如人也罢,你都要试着安静下来,去做自己该做的事,而不是让内心的烦躁、焦虑,坏掉你本来就不多的热情和定力