
2017电赛国赛滚球控制系统摄像头部分(精度误差0.5cm左右)
发布于2019-08-06 11:19 阅读(1231) 评论(0) 点赞(3) 收藏(2)
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
def ban_detect(contours):
for cnt in range(len(contours)):
arcLength = cv2.arcLength(contours[cnt], True)
if arcLength > 1000:
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[cnt], arcLength * 0.02, 1)
cv2.polylines(image, [approx], True, (0, 0, 255), 2)
mm = cv2.moments(approx)
cx = int(mm['m10'] / mm['m00'])
cy = int(mm['m01'] / mm['m00'])
cv2.circle(image, (cx, cy), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
print("板的中心坐标是 (%d,%d)" % (np.int(cx), np.int(cy)))
# cv2.drawContours(image, contours, cnt, (0, 255, 0), 2)
def ball_detect(contours): # 漏油点定位
arclengthMin = 100
arclengthMax = 300
squareMin = 600
squareMax = 1000
point_flag = False
for cnt in range(len(contours)):
square = cv2.contourArea(contours[cnt])
arcLength = cv2.arcLength(contours[cnt], True)
# print(square, arcLength)
epsilon = 0.01 * arcLength # 轮廓逼近,主要是对闭合轮廓进行检测,即水管的漏油点
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[cnt], epsilon, True) # 进行图像拟合
corners = len(approx) # 分析几何形状,如果图像的角大于10即为圆形
if corners > 10 and arcLength > arclengthMin and arcLength < arclengthMax and square > squareMin and square < squareMax:
rrt = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[cnt]) # 椭圆拟合
cv2.ellipse(image, rrt, (0, 0, 255), 2, cv2.LINE_AA) # 画出拟合椭圆
x, y = rrt[0] # 求出椭圆中心
print("球的坐标是 (%d,%d)" % (np.int(x), np.int(y)))
cv2.circle(image, (np.int(x), np.int(y)), 4, (255, 0, 0), -1, 8, 0) # 画出椭圆中心
point_flag = True
return point_flag
def blurred_image(binary):
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary, (3, 3), 0) # 滤波处理
# cv2.imshow("blurred",blurred) #显示滤波图像
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (7, 7))
closed = cv2.morphologyEx(blurred, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# cv2.imshow("closed",closed)
# 所得图像仍有许多白点,通过腐蚀和膨胀去除白点,最后一个参数是腐蚀的次数
closed = cv2.erode(closed, None, iterations=6)
# cv2.imshow("closed1",closed)
closed = cv2.dilate(closed, None, iterations=6)
# cv2.imshow("closed2", closed)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(closed, 250, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
# cv2.imshow("binary", binary)
edges = cv2.Canny(binary, 50, 120) # 使用Canny进行轮廓检测
# cv2.imshow("Canny",edges)
return edges
def Camera_analysis(image):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.imshow("gray",gray)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 130, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化,板
ret, binary1 = cv2.threshold(gray, 30, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化,球
edges1 = blurred_image(binary)
edges2 = blurred_image(binary1)
contours1, hierarchy1 = cv2.findContours(edges1, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 对轮廓图进行边缘检测
contours2, hierarchy2 = cv2.findContours(edges2, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 对轮廓图进行边缘检测
ban_detect(contours1)
ball_detect(contours2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
image = cv2.imread("./image/ban2.jpg")
Camera_analysis(image)
cv2.imshow("image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
通过该代码可以确定板的中心与球的位置

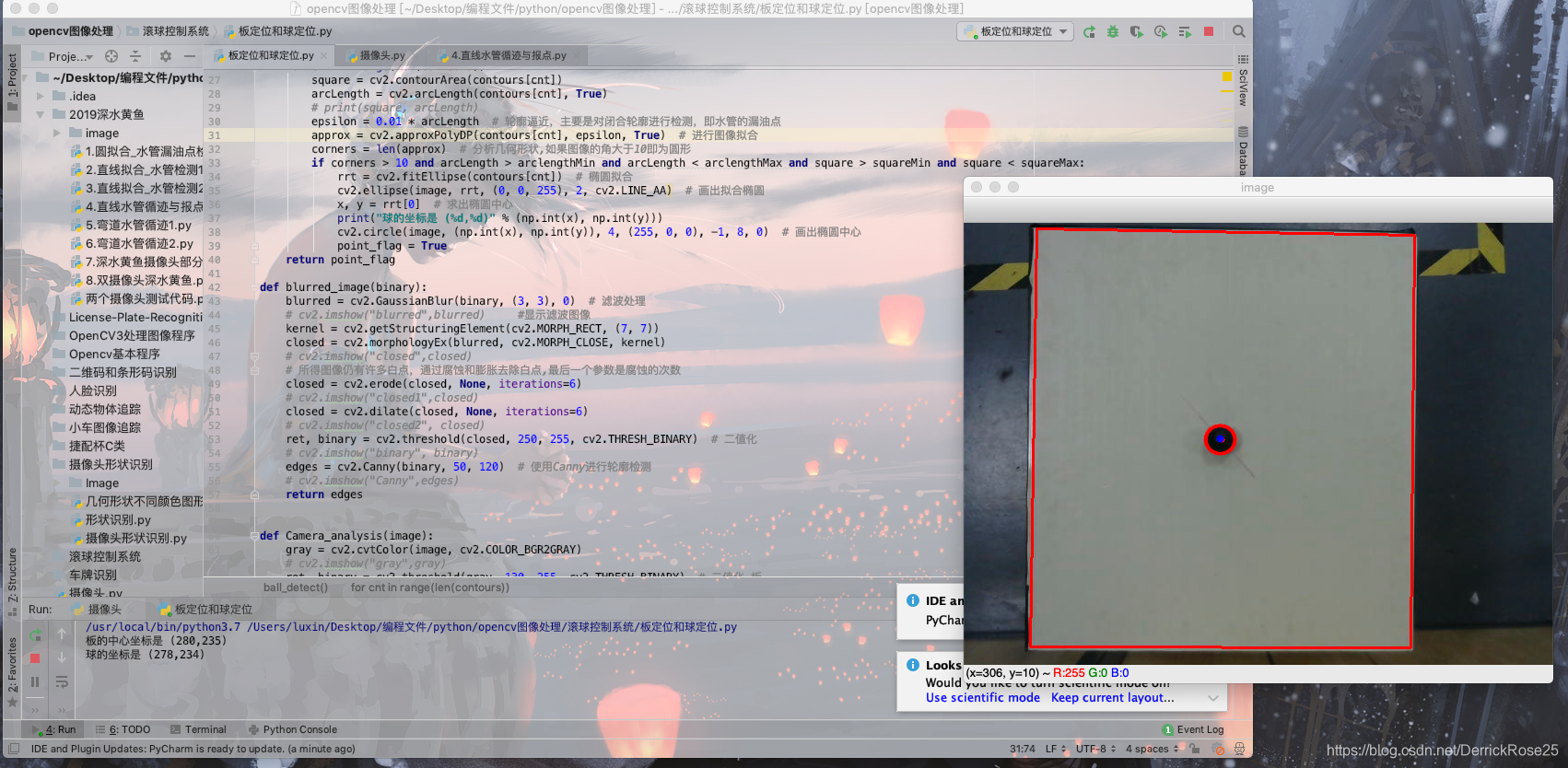
经过一系列数学分析和线性求解,以板的左上角建立直角坐标系,可以准确确定球的位置,单位是厘米,存在些许误差但是影响不大,代码如下
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
def pt_line_distance(ball_x, ball_y, k, b):
distance = abs((k * ball_x - ball_y + b) / math.sqrt(k * k + 1))
# print(distance)
return distance
def get_line(point1, point2): # 求直线方程 y = kx + b
k = (point1[1] - point2[1]) / (point1[0] - point2[0])
b = point1[1] - k * point1[0]
return k, b
def ban_detect(contours):
for cnt in range(len(contours)):
arcLength = cv2.arcLength(contours[cnt], True)
if arcLength > 1000:
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[cnt], arcLength * 0.02, 1)
# print(approx)
# cv2.polylines(image, [approx], True, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 求板子的中心
mm = cv2.moments(approx)
cx = int(mm['m10'] / mm['m00'])
cy = int(mm['m01'] / mm['m00'])
cv2.circle(image, (cx, cy), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# print("板的图像中心坐标是 (%d,%d)" % (np.int(cx), np.int(cy)))
k1, b1 = get_line(approx[1][0], approx[0][0])
k2, b2 = get_line(approx[1][0], approx[2][0])
return k1, b1, k2, b2
# print(k1, b1, k2, b2)
# 求板的顶点坐标
# for app in range(len(approx)):
# x = approx[app][0][0]
# y = approx[app][0][1]
# cv2.circle(image, (x,y), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# cv2.putText(image, 'num:%d' % (app), (x + 30, y + 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 0, 255), 4)
def ball_detect(contours): # 漏油点定位
arclengthMin = 80
arclengthMax = 100
squareMin = 500
squareMax = 700
for cnt in range(len(contours)):
square = cv2.contourArea(contours[cnt])
arcLength = cv2.arcLength(contours[cnt], True)
# print(square, arcLength)
epsilon = 0.01 * arcLength # 轮廓逼近,主要是对闭合轮廓进行检测,即水管的漏油点
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[cnt], epsilon, True) # 进行图像拟合
corners = len(approx) # 分析几何形状,如果图像的角大于10即为圆形
if corners > 10 and arcLength > arclengthMin and arcLength < arclengthMax and square > squareMin and square < squareMax:
rrt = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[cnt]) # 椭圆拟合
cv2.ellipse(image, rrt, (0, 0, 255), 2, cv2.LINE_AA) # 画出拟合椭圆
x, y = rrt[0] # 求出椭圆中心
# print("球的图像坐标是 (%d,%d)" % (np.int(x), np.int(y)))
cv2.circle(image, (np.int(x), np.int(y)), 4, (255, 0, 0), -1, 8, 0) # 画出椭圆中心
return (np.int(x), np.int(y))
def blurred_image(binary):
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(binary, (3, 3), 0) # 滤波处理
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (7, 7))
closed = cv2.morphologyEx(blurred, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# 所得图像仍有许多白点,通过腐蚀和膨胀去除白点,最后一个参数是腐蚀的次数
closed = cv2.erode(closed, None, iterations=6)
closed = cv2.dilate(closed, None, iterations=6)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(closed, 250, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
edges = cv2.Canny(binary, 50, 120) # 使用Canny进行轮廓检测
return edges
def Camera_analysis(image):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cv2.imshow("gray",gray)
ret, binary1 = cv2.threshold(gray, 130, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化,板
ret, binary2 = cv2.threshold(gray, 30, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化,球
edges1 = blurred_image(binary1)
edges2 = blurred_image(binary2)
contours1, hierarchy1 = cv2.findContours(edges1, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 对轮廓图进行边缘检测
contours2, hierarchy2 = cv2.findContours(edges2, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 对轮廓图进行边缘检测
k1, b1, k2, b2 = ban_detect(contours1)
ball_x, ball_y = ball_detect(contours2)
y = int((pt_line_distance(ball_x, ball_y, k1, b1))/6.6451)
x = int((pt_line_distance(ball_x, ball_y, k2, b2))/6.0923)
# print(k1, b1, k2, b2)
# 以板的左上角为坐标原点建立直角坐标系
print("球在板上的坐标为 (%d,%d)"%(x,y))
# print(ball_x,ball_y)
if __name__ == "__main__":
image = cv2.imread("./image/ban4.jpg")
Camera_analysis(image)
cv2.imshow("image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# if __name__ == "__main__":
# # 初始化摄像头
# cameraCapture = cv2.VideoCapture('http://192.168.12.1:8080/?action=stream') # 树莓派地址
# # cameraCapture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# while True:
# # 获取当前帧
# ret, image = cameraCapture.read()
# Camera_analysis(image)
# cv2.imshow("frame", image)
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
# break
# cameraCapture.release()
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
效果: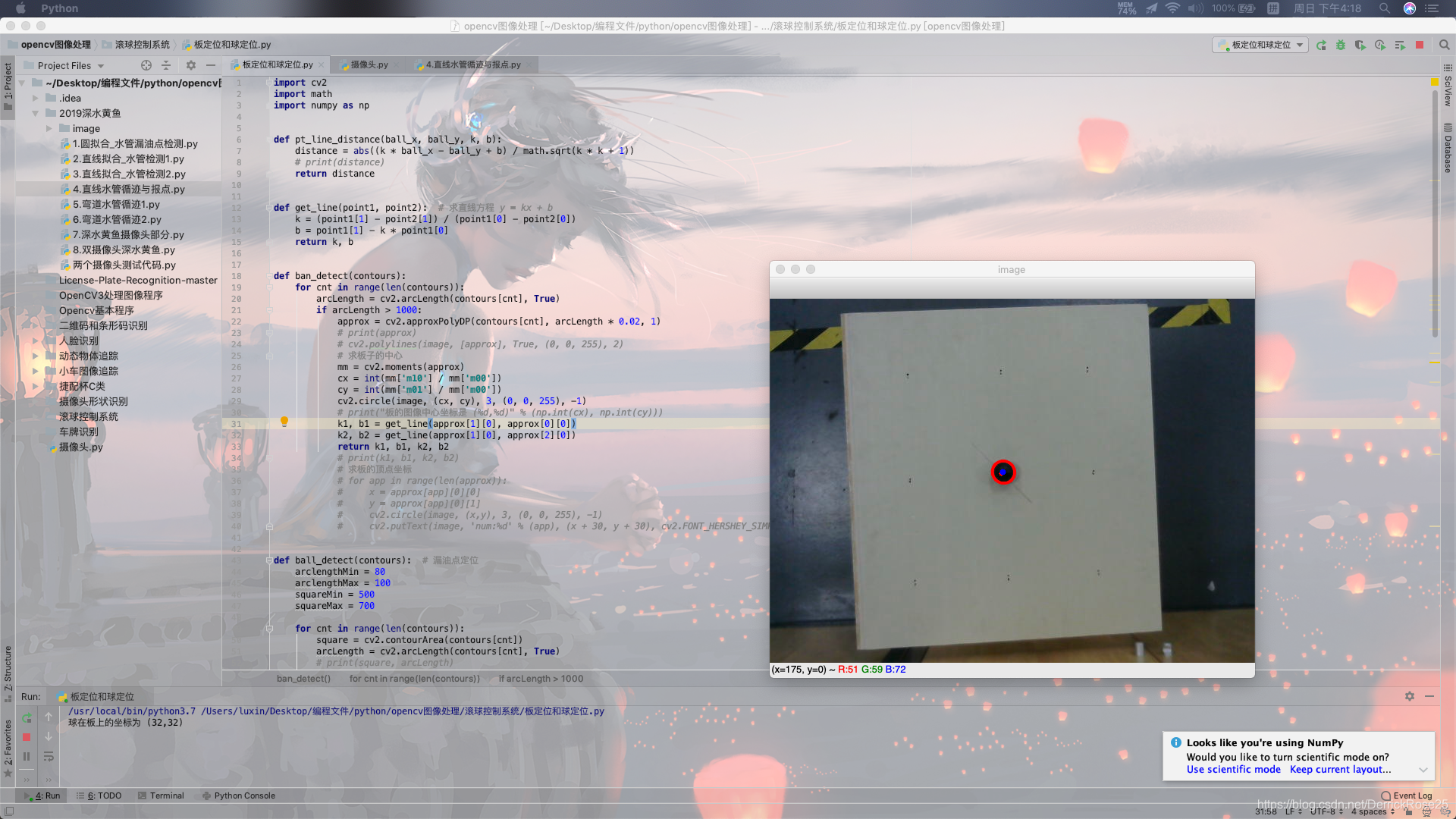
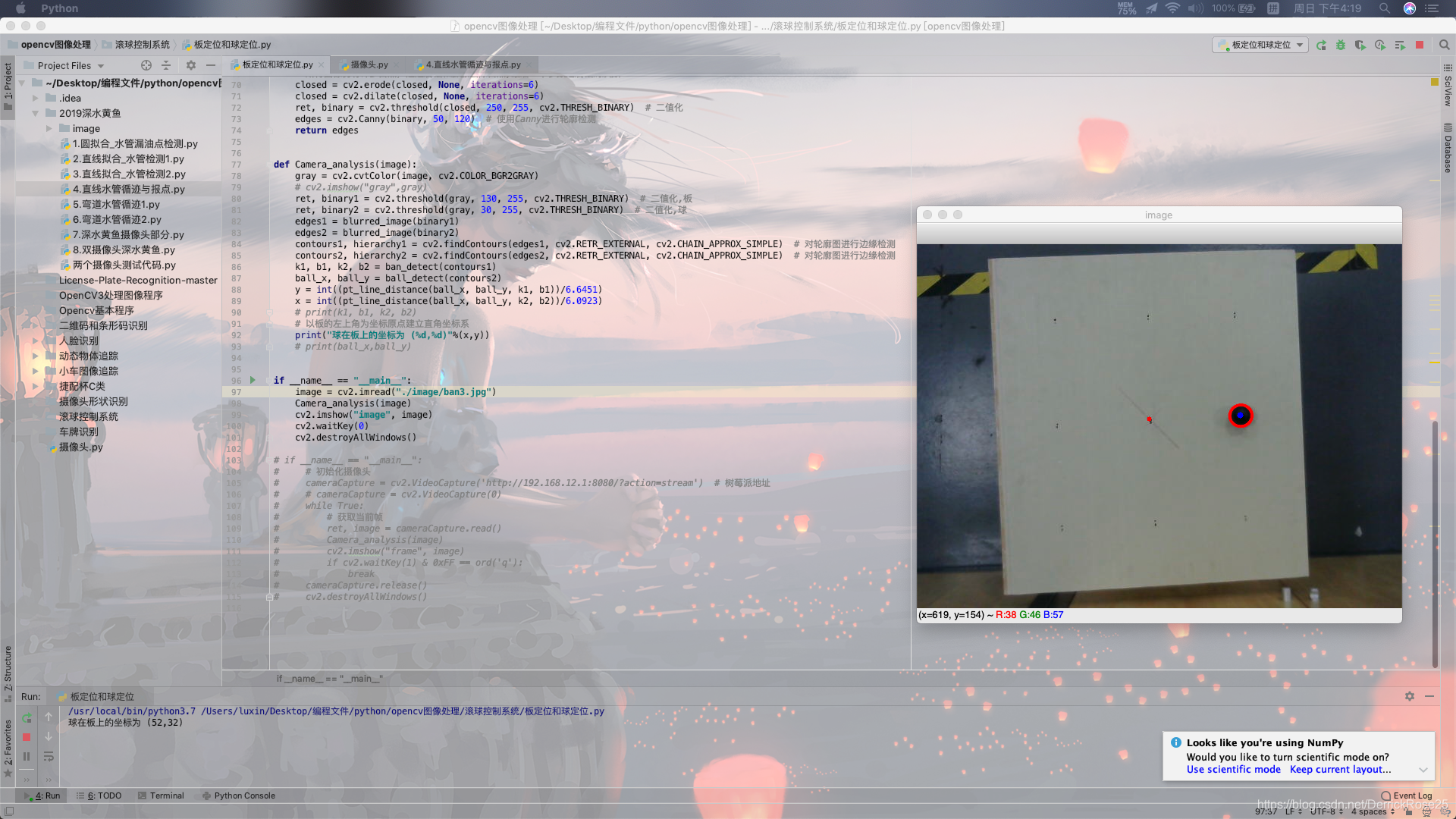
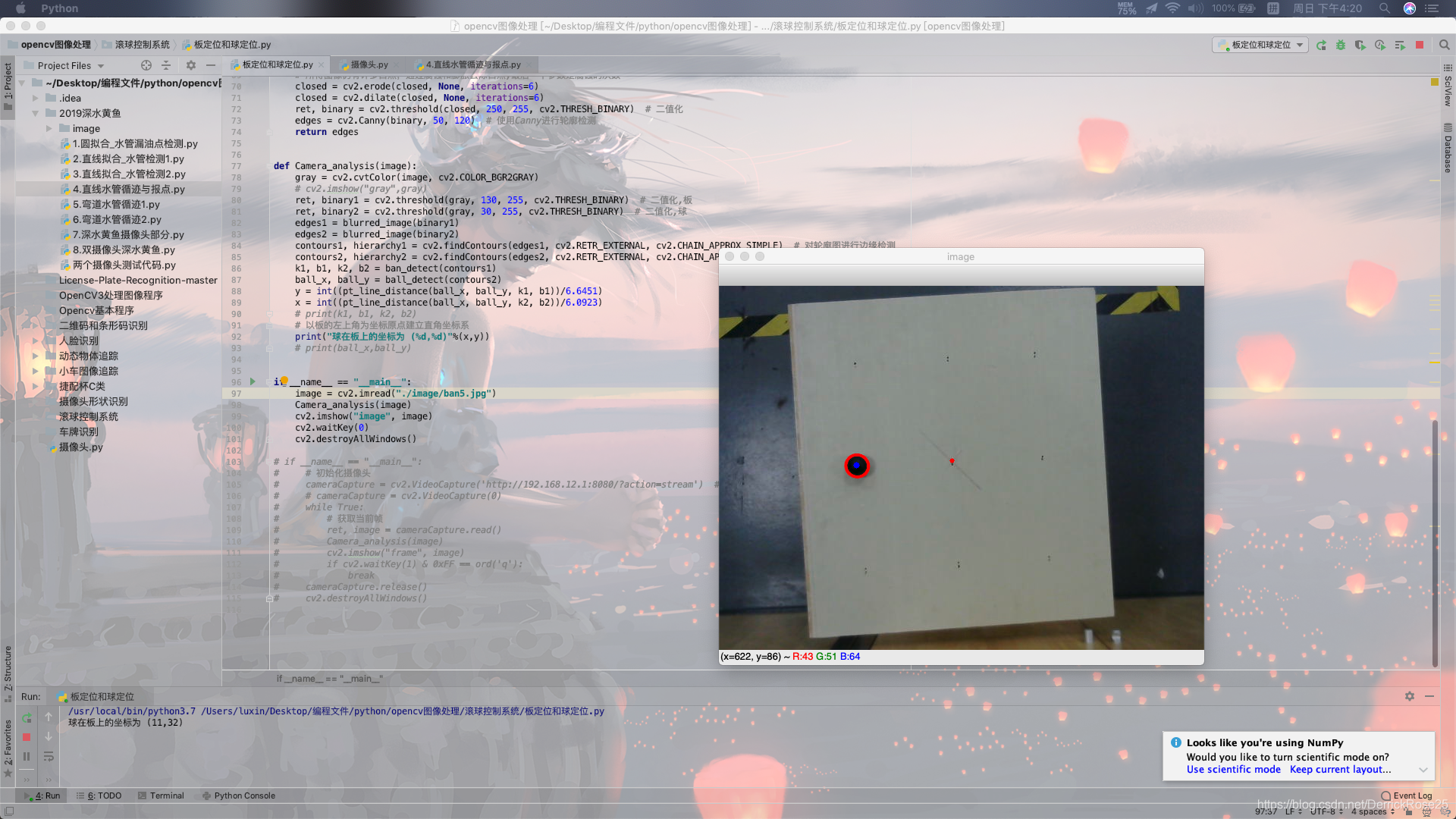
将代码移植到树莓派上即可使用
舵机PID控制代码及调试过程见本人博客:https://blog.csdn.net/DerrickRose25/article/details/97285392
所属网站分类: 技术文章 > 博客
作者:yoyo
链接:https://www.pythonheidong.com/blog/article/8293/8dbc2a3bcd78d72082d2/
来源:python黑洞网
任何形式的转载都请注明出处,如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
昵称:
评论内容:(最多支持255个字符)
---无人问津也好,技不如人也罢,你都要试着安静下来,去做自己该做的事,而不是让内心的烦躁、焦虑,坏掉你本来就不多的热情和定力